Generic Name
Composition
Therapeutic Category
Division
Azithromycin Dihydrate
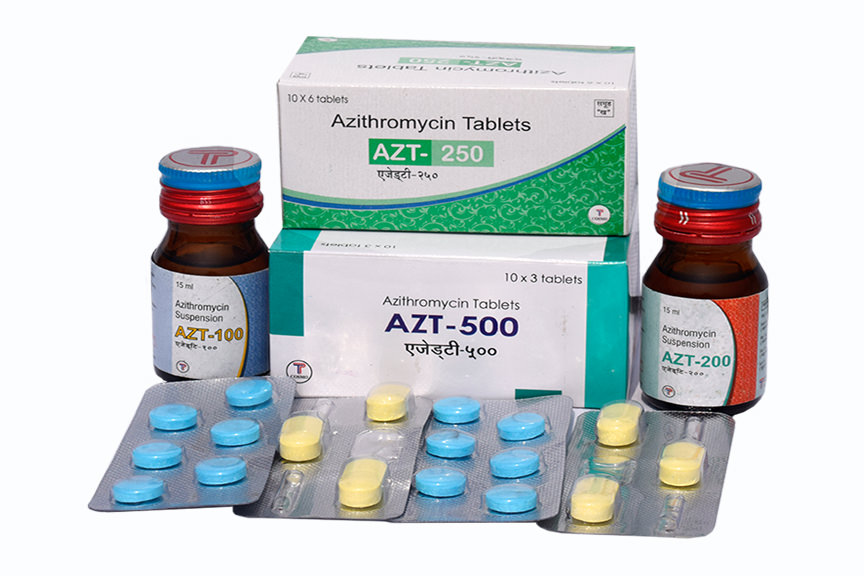
Azithromycin 250mg Tablets
Azithromycin 500 mg Tablets
Azithromycin 100 mg/5ml Suspension
Azithromycin 200mg/5ml Suspension
Macrolide Antibiotic
COSMO
| BRAND | COMPOSITION | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|
|
AZT 100 SUSPENSION |
Each 5 ml of suspension contains: Azithromycin USP as Dihydrate eq. to Azithromycin anhydrous 100mg |
Orange colored, flavored suspension filled in 20 ml amber bottle and sealed with ROPP cap. |
|
AZT 200 SUSPENSION |
Each 5 ml of suspension contains: Azithromycin USP as Dihydrate eq. to Azithromycin anhydrous 200mg |
Orange colored, flavored suspension filled in 20 ml amber bottle and sealed with ROPP cap. |
|
AZT 250 |
Each film coated tablet contains: Azithromycin USP as Dihydrate eq. to Azithromycin anhydrous 250mg |
Light blue, round, biconvex, film-coated tablet. |
|
AZT 500 |
Each film coated tablet contains: Azithromycin USP as Dihydrate eq. to Azithromycin anhydrous 500mg |
Light yellow, oblong, film-coated tablet with breakline in one side. |
PHARMACOLOGY
Pharmacotherapeutic Group: Macrolide antibiotic
Pharmacodynamic properties: AZT (Azithromycin) is an azalide, a sub-class of the macrolide antibiotics. By binding to the 50S ribosomal subunit, AZT inhibits the translocation of peptide chains from one side of the ribosome to the other. As a consequence of this, RNA dependent protein synthesis in sensitive organisms is prevented resulting in inhibition of bacterial growth.
Pharmacodynamic properties: AZT (Azithromycin) is a semi synthetic macrolide antibiotic of azalide class. AZT inhibits bacterial protein synthesis by binding to the 50S ribosomal subunit of the bacterial ribosome. This binding inhibits peptidyl transferase activity and interferes with amino acid translocation during the process of translation this resulting in inhibition of bacterial growth.
Pharmacokinetic properties:
Absorption: Rapidly absorbed from the GI tract; Absolute bioavailability: Approx 34-52%; Time to peak plasma concentration: 2-3 hr
Distribution: Extensive into the tissues (higher than those in blood), WBC (high concentrations), CSF (small amounts); Plasma protein binding (concentration dependent)
Metabolism: Hepatic metabolism via demethylation (microbiologically inactive)
Excretion: Via bile (as unchanged drug and inactive metabolites); urine (approx 6% of oral dose); Terminal elimination half-life: 2-4days
INDICATIONS
Acute bacterial sinusitis; Otitis media; Acute exacerbation of chronic bronchitis; Tonsillitis/Pharyngitis; Community acquired pneumonia; Skin and soft tissue infection; Acne; Sexually transmitted disease.
DOSE
The dose of AZT is 1500mg to be administered as 500mg once daily for 3 consecutive days. Alternatively 500mg as a single dose on the 1st day followed by 250mg once daily for 4 days may be given.
Uncomplicated chlamydia trachomatis urethritis and cervicitis: The dosage is 1000mg as a single oral dose.
Children under 45kg: 10mg/kg given as single dose for 3 days.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Known hypersensitivity to azithromycin, erythromycin, any macrolide or ketolide antibiotic; Co-administration with pimozide; History of cholestatic jaundice/hepatic dysfunction associated with prior use of azithromycin; Severe liver disease.
SPECIAL PRECAUTIONS
May increase the risk of torsades de pointes and fatal heart arrhythmias in patients with prolonged QT interval, low K or Mg blood levels, slow heart rate and medication treating abnormal heart rhythms; Impaired hepatic and renal function; Pregnancy and lactation.
ADVERSE DRUG REACTIONS
GI disturbances, visual impairment, irritation, deafness, dizziness, headache, fatigue, anorexia, paraesthesia, dysgeusia, nasal congestion, sinusitis, facial swelling, periocular swelling, pruritus, rash, urticaria, arthralgia, vaginitis. Potentially Fatal: Angioedema and cholestatic jaundice.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
Increases serum concentrations of digoxin, ciclosporin, terfenadine, hexobarbital and phenytoin; Decreased rate of absorption with antacids containing aluminium and magnesium; Increased risk of ergot toxicity. Potentially Fatal: Increased risk of cardiotoxicity with pimozide.
PATIENT INFORMATION |
|---|
|
Administration:
Pregnancy: Category B Nursing Mother: AZT is partially passed through mother's milk hence should not be used during breastfeeding. Storage: Store the tablet and suspension at room temperature away from light and moisture; Do not refrigerate or freeze; Keep out of reach of children. Missed dose: If you have missed a dose, take that dose as quickly as possible, however, if it is almost time for your next dose, then skip the missed dose and take your next dose at the normal time; Do not take a double dose to make up for a forgotten dose. |
AZT 100 SUSPENSION: Each bottle contains 15ml of suspension.
AZT 200 SUSPENSION: Each bottle contains 15ml of suspension.
AZT 250: Each box contains 10 strip packs of 6 tablets per strip.
AZT 500: Each box contains 10 strip packs of 3 tablets per strip.